DOMAIN :
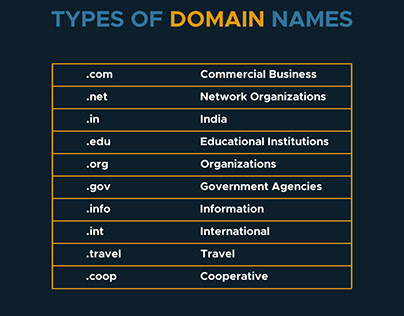
In web designing, a “Domain” refers to the unique name that identifies a website on the internet. It’s the part of a web address that comes after “www.” For example, in the web address “www.odmt.in,” “odmt.in” is the domain. This domain is what users type into their browsers to access a specific website. Additionally, domains can have different extensions like “.com,” “.in “.org,” “.net,” etc.
How to Register Your Domain :
When building a website, choosing and registering a domain name is usually the first step. The process of registering a domain name is described below.
- Find a Domain Name Registrar: Domain name registrars, such as GoDaddy, Bluehost, and Domain.com, sell and manage domain names.
- Search for a Domain Name: Here, you can use your domain name registrar to search for an available domain name. Make sure to incorporate important keywords when appropriate.
- Choose a Domain Name Suffix: After you’ve chosen a domain name, the next step is to choose a suffix. The most popular is .com, but other common ones in the U.S. include .net and .org.
- Purchase a Domain Name: Once you’ve chosen your domain name and suffix, you need to purchase it through the domain registrar. What usually happens is you pay for the domain for a year and then consistently pay to renew it.
- Include Domain ID protection: When registering a domain name, you must include information like name, phone number, physical address, and email address, which will become public once your domain name has been registered. To protect yourself, you can purchase domain privacy, which will shield your information from spammers or identity thieves.
SUB-DOMAIN :
- A subdomain specifies a separate division from a parent domain within the same servers. Therefore, you don’t need to register a subdomain if you already own the domain.
- A subdomain may also be called a hostname. The www part in most URLs is technically a subdomain, suggesting that a website is part of the World Wide Web. However, some websites have an additional subdomain besides the hostname.
- A common reason to create subdomains is to organize web content into separate sections. For example, Google uses developers.google.com to provide information specifically for developers.
- A subdomain is also useful for localization. Take Wikipedia, for example. It has a subdomain for different languages – en.wikipedia.org for the English version and de.wikipedia.org for the German one.
- We can create multiple subdomains for a main domain.

